What is Angina?
Manifesting as chest pains, angina results when the blood supply that is meant to reach the muscles in the heart becomes restricted. The typical reason for this is that the arteries leading to the affected muscles have become hardened somehow, a condition known as atherosclerosis.
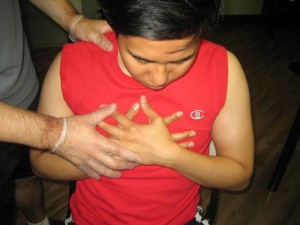
Typically brought on by physical activity, the pain that is experienced during such attacks causes a tightening within the chest, left arm, and sometimes even spreads to the neck and jaw. Unlike a true heart attack, angina lasts only a few minutes and is not necessarily fatal on its own.
The 2 Types of Angina
There are two very identifiable types of angina, and those are:
1) Stable angina
While this type is not necessarily fatal, it is a warning sign and should be treated as such. Exercise and/or stress can bring this type on, but through medication and rest it is possible to alleviate the symptoms.
2) Unstable angina
This type of angina has no warning signs and can strike at any time. Even after resting it doesn’t go away, and it is always necessary to treat this type as a medical emergency. This can increase the risk of suffering a stroke or a heart attack if an individual does not take measures to take care of the problem.
How to Treat Angina
Any and all treatment for angina will typically require at least a moderate change in lifestyle and dietary habits, depending on the advice of the consulting physician. There are a large number of medications that have been developed to specifically treat and alleviate the risk of angina, though careful monitoring of this condition is still necessary. Surgeries that exist to relieve the effects of angina is often considered if medications fail to have the desired effect, but are not a first choice and can be limited in effect depending on the patient.
Complications of Angina
One very serious concern with those who suffer from angina is that one of the triggers, the development of atherosclerosis, will continually get worse and eventually close off the arteries necessary for delivering blood throughout their body. If arteries attempting to bring blood to the brain become blocked they could suffer a stroke, and if the arteries pumping blood through heart became blocked, a heart attack would result.
The current statistics state that at least 1 out of 100 individuals who experience stable angina will endure a fatal stroke or heart attack, while 1 out of 40 will suffer through a non-life threatening attack. As has been stated above it is highly recommended for anyone suffering through angina to seriously consider a change in lifestyle.
Who Does Angina Affect Most?
Angina is most commonly seen to affect older adults, particularly men.
